LESSON 1: Basic tasks in Excel for Windows
Create a new workbook
Excel documents are called workbooks. Each workbook has sheets, typically called spreadsheets. You can add as many sheets as you want to a workbook, or you can create new workbooks to keep your data separate.-
Click File, and then click New.
-
Under New, click the Blank workbook.
Enter your data
-
Click an empty cell.For example, cell A1 on a new sheet. Cells are referenced by their location in the row and column on the sheet, so cell A1 is in the first row of column A.
-
Type text or a number in the cell.
-
Press Enter or Tab to move to the next cell.
Use AutoSum to add your data
When you’ve entered numbers in your sheet, you might want to add them up. A fast way to do that is by using AutoSum.-
Select the cell to the right or below the numbers you want to add.
-
Click the Home tab, and then click AutoSum in the Editing group.
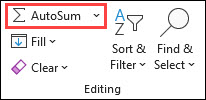
AutoSum adds up the numbers and shows the result in the cell you selected.
Create a simple formula
Adding numbers is just one of the things you can do, but Excel can do other math as well. Try some simple formulas to add, subtract, multiply, or divide your numbers.-
Pick a cell, and then type an equal sign (=).That tells Excel that this cell will contain a formula.
-
Type a combination of numbers and calculation operators, like the plus sign (+) for addition, the minus sign (-) for subtraction, the asterisk (*) for multiplication, or the forward slash (/) for division.For example, enter =2+4, =4-2, =2*4, or =4/2.
-
Press Enter.This runs the calculation.
You can also press Ctrl+Enter if you want the cursor to stay on the active cell.
Apply a number format
To distinguish between different types of numbers, add a format, like currency, percentages, or dates.-
Select the cells that have numbers you want to format.
-
Click the Home tab, and then click the arrow in the General box.
-
Pick a number format.

If you don’t see the number format you’re looking for, click More Number Formats.
Put your data in a table
A simple way to access Excel’s power is to put your data in a table. That lets you quickly filter or sort your data.-
Select your data by clicking the first cell and dragging to the last cell in your data.To use the keyboard, hold down Shift while you press the arrow keys to select your data.
-
Click the Quick Analysis button
 in the bottom-right corner of the selection.
in the bottom-right corner of the selection.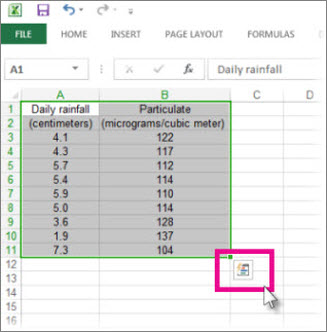
-
Click Tables, move your cursor to the Table button to preview your data, and then click the Table button.

-
Click the arrow
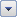 in the table header of a column.
in the table header of a column. -
To filter the data, clear the Select All check box, and then select the data you want to show in your table.
-
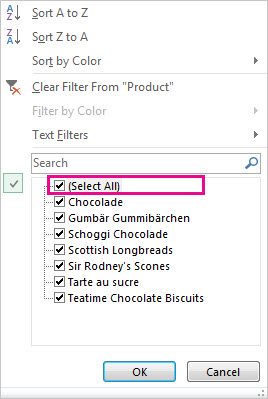
To sort the data, click Sort A to Z or Sort Z to A.
-
Click OK.
Show totals for your numbers
Quick Analysis tools let you total your numbers quickly. Whether it’s a sum, average, or count you want, Excel shows the calculation results right below or next to your numbers.-
Select the cells that contain numbers you want to add or count.
-
Click the Quick Analysis button
 in the bottom-right corner of the selection.
in the bottom-right corner of the selection. -
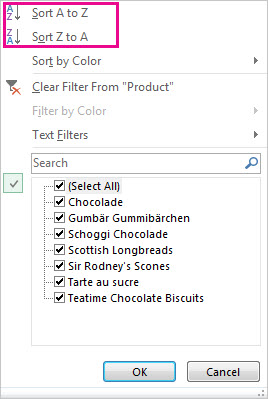
Click Totals, move your cursor across the buttons to see the calculation results for your data, and then click the button to apply the totals.
Add meaning to your data
Conditional formatting or sparklines can highlight your most important data or show data trends. Use the Quick Analysis tool for a Live Preview to try it out.-
Select the data you want to examine more closely.
-
Click the Quick Analysis button
 in the bottom-right corner of the selection.
in the bottom-right corner of the selection. -
Explore the options on the Formatting and Sparklines tabs to see how they affect your data.
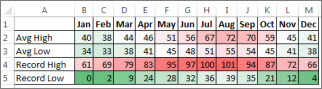
For example, pick a color scale in the Formatting gallery to differentiate high, medium, and low temperatures.
-
When you like what you see, click that option.
Show your data in a chart
The Quick Analysis tool recommends the right chart for your data and gives you a visual presentation in just a few clicks.-
Select the cells that contain the data you want to show in a chart.
-
Click the Quick Analysis button
 in the bottom-right corner of the selection.
in the bottom-right corner of the selection. -
Click the Charts tab, move across the recommended charts to see which one looks best for your data, and then click the one that you want.

Note: Excel shows different charts in this gallery, depending on what’s recommended for your data.
Save your work
-
Click the Save button on the Quick Access Toolbar, or press Ctrl+S.
If you’ve saved your work before, you’re done.
-
If this is the first time you've save this file:
-
Under Save As, pick where to save your workbook, and then browse to a folder.
-
In the File name box, enter a name for your workbook.
-
Click Save.
-
Print your work
-
Click File, and then click Print, or press Ctrl+P.
-
Preview the pages by clicking the Next Page and Previous Page arrows.

The preview window displays the pages in black and white or in color, depending on your printer settings.
If you don’t like how your pages will be printed, you can change page margin.
-
Click Print.

ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon